Integrate Langfuse with CrewAI
This notebook provides a step-by-step guide on integrating Langfuse with CrewAI to achieve observability and debugging for your LLM applications.
What is CrewAI? CrewAI (GitHub) is a framework for orchestrating autonomous AI agents. CrewAI enables you to create AI teams where each agent has specific roles, tools, and goals, working together to accomplish complex tasks. Each member (agent) brings unique skills and expertise, collaborating seamlessly to achieve your objectives.
What is Langfuse? Langfuse is an open-source LLM engineering platform. It offers tracing and monitoring capabilities for AI applications. Langfuse helps developers debug, analyze, and optimize their AI systems by providing detailed insights and integrating with a wide array of tools and frameworks through native integrations, OpenTelemetry, and dedicated SDKs.
Getting Started
Let’s walk through a practical example of using CrewAI and integrating it with Langfuse for comprehensive tracing.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
%pip install langfuse crewai openinference-instrumentation-crewai -qStep 2: Configure Langfuse SDK
Next, set up your Langfuse API keys. You can get these keys by signing up for a free Langfuse Cloud account or by self-hosting Langfuse. These environment variables are essential for the Langfuse client to authenticate and send data to your Langfuse project.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-***"
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-***"
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-***"With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Verify connection
if langfuse.auth_check():
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
else:
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")
Step 3: Initialize CrewAI Instrumentation
Now, we initialize the OpenInference instrumentation SDK to automatically capture CrewAI operations and export OpenTelemetry (OTel) spans to Langfuse.
from openinference.instrumentation.crewai import CrewAIInstrumentor
CrewAIInstrumentor().instrument(skip_dep_check=True)Step 4: Basic CrewAI Application
Let’s create a straightforward CrewAI application. In this example, we’ll create a simple crew with agents that can collaborate to complete tasks. This will serve as the foundation for demonstrating Langfuse tracing.
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
# Define your agents with roles and goals
coder = Agent(
role='Software developer',
goal='Write clear, concise code on demand',
backstory='An expert coder with a keen eye for software trends.',
)
# Create tasks for your agents
task1 = Task(
description="Define the HTML for making a simple website with heading- Hello World! Langfuse monitors your CrewAI agent!",
expected_output="A clear and concise HTML code",
agent=coder
)
# Instantiate your crew
crew = Crew(
agents=[coder],
tasks=[task1],
)
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(as_type="span", name="crewai-index-trace"):
result = crew.kickoff()
print(result)
langfuse.flush()Step 5: View Traces in Langfuse
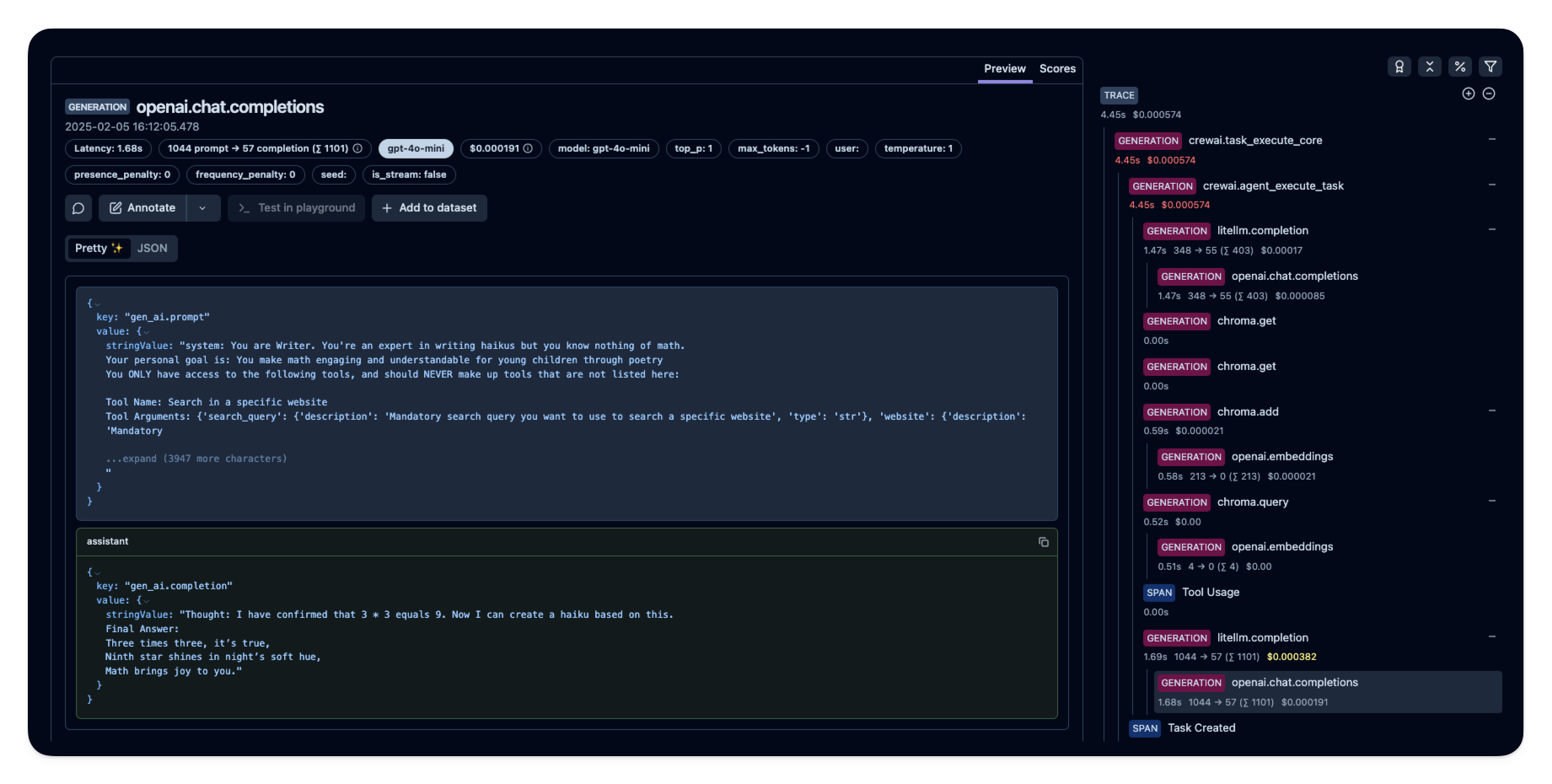
After executing the application, navigate to your Langfuse Trace Table. You will find detailed traces of the application’s execution, providing insights into the LLM calls, agent operations, inputs, outputs, and performance metrics. The trace will show the complete flow from task processing through agent collaboration to response generation.
Interoperability with the Python SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse SDKs to add additional attributes to the trace.
The @observe() decorator provides a convenient way to automatically wrap your instrumented code and add additional attributes to the trace.
from langfuse import observe, propagate_attributes, get_client
langfuse = get_client()
@observe()
def my_llm_pipeline(input):
# Add additional attributes (user_id, session_id, metadata, version, tags) to all spans created within this execution scope
with propagate_attributes(
user_id="user_123",
session_id="session_abc",
tags=["agent", "my-trace"],
metadata={"email": "user@langfuse.com"},
version="1.0.0"
):
# YOUR APPLICATION CODE HERE
result = call_llm(input)
# Update the trace input and output
langfuse.update_current_trace(
input=input,
output=result,
)
return resultLearn more about using the Decorator in the Langfuse SDK instrumentation docs.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application: